

While in diamond, the adjacent atoms are covalently bonded with each other. That means graphite has delocalized electrons which are responsible for electric current.Īlso, these delocalized electrons absorb most of the light.Īnd as the light is absorbed, it appears shiny black in color. You might be knowing that graphite is a good conductor of electricity. Now, for graphite and diamond, the entire concept is based on how the electrons are bonded with each other. If the object absorbs all the light, then it will appear completely black.Īnd if the object does not absorb any light (or it reflects all the light), then it will appear completely white. The color of any substance depends upon the light absorption by the object. HEX (Hexagonal) Density Graphite: 2.267 g/cm 3ĭiamond: 3.515 g/cm 3 Main isotope of Carbon 12C, 13C, 14C CAS number Graphite:
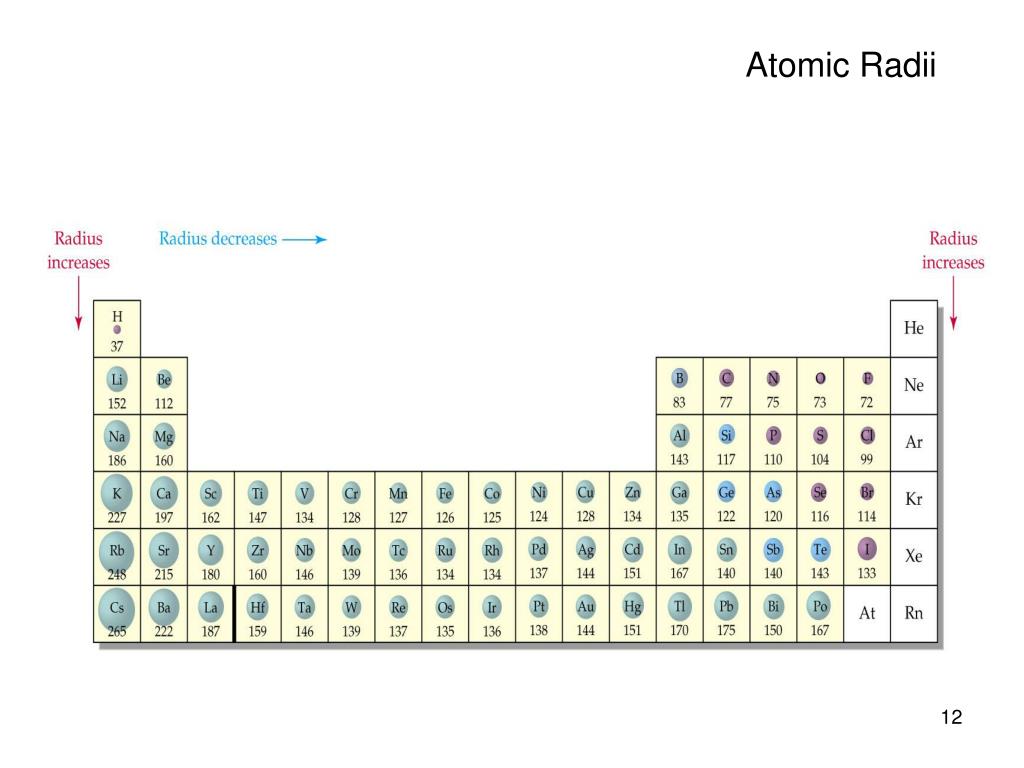
Protons in Carbon 6 Neutrons in Carbon 6 Electrons in Carbon 6 Symbol of Carbon C Atomic mass of CarbonĢ, 4 Electronic configuration of Carbon 2s 2 2p 2 Atomic radius of Carbonġ70 picometers (van der Waals radius) Valence electrons in CarbonĤ 1st Ionization energy of Carbon 11.26 eV Electronegativity of CarbonĢ.55 (Pauling scale) Crystal structure of Carbon Group: 14, Period: 2, Block: p Category of Carbon element Carbon Element (C) Information Appearance of CarbonĪppearance of diamond: Clear State of Carbon at STP Solid Position of Carbon in Periodic table So if you want to know anything about Carbon element, then this guide is for you. In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Carbon element in Periodic table.) This is a SUPER easy guide on Carbon element.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
